The historical auto loan rates in Canada have played a significant role in shaping the affordability of vehicle ownership for Canadians over the years. Understanding how these rates have evolved provides valuable insights for prospective car buyers, financial planners, and policymakers. Auto loan rates are influenced by economic factors such as inflation, Bank of Canada policies, and market competition, making their historical trends a fascinating subject for analysis.
This article dives deep into the patterns, drivers, and implications of past auto loan rates, leveraging authoritative resources like government and bank websites to provide a comprehensive overview. For those looking to explore current financing options, Quick Approvals offers a user-friendly platform to navigate auto loan solutions.
Historical Trends of Auto Loan Rates in Canada: A Timeline
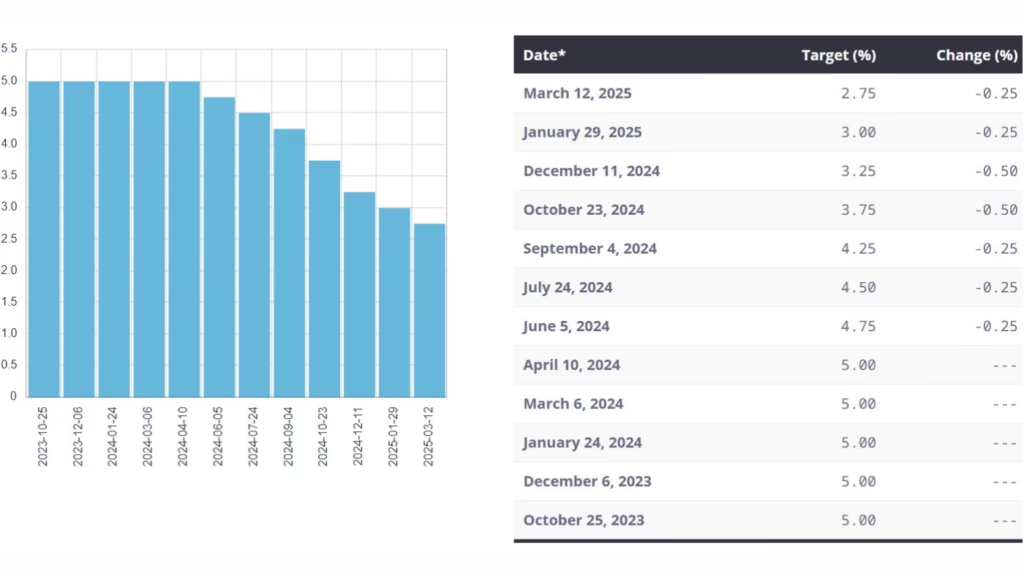
historical auto loan rates in Canada, Auto loan rates in Canada have fluctuated significantly over the decades, reflecting broader economic conditions. The historical trends of auto loan rates in Canada reveal periods of high and low interest rates driven by factors like monetary policy, economic recessions, and global events.
- 1980s: The early 1980s saw some of the highest auto loan rates in Canadian history, with rates peaking at 15-20% due to rampant inflation and tight monetary policies. The Bank of Canada raised its key interest rate to combat inflation, directly impacting borrowing costs.
- 1990s: Rates began to decline as inflation stabilized, averaging 8-12%. The economic recovery post-1990 recession allowed for more competitive lending environments.
- 2000s: The early 2000s marked a period of relative stability, with rates hovering between 6-9%. However, the 2008 financial crisis led to a sharp drop in rates as the Bank of Canada slashed its benchmark rate to stimulate the economy, resulting in auto loan rates dipping to 4-6%.
- 2010s: Post-crisis recovery saw rates remain low, often between 3-5%, with promotional offers from manufacturers dropping to 0-2% for qualified buyers. This era was marked by increased competition among lenders.
- 2020s: The COVID-19 pandemic introduced unprecedented challenges, with rates initially dropping to historic lows (1-3%) in 2020-2021 due to economic stimulus measures. However, as inflation surged in 2022-2023, the Bank of Canada raised rates, pushing average auto loan rates to 5-8% by 2025.
These trends highlight the cyclical nature of auto loan rates, closely tied to the Bank of Canada’s monetary policy, accessible via Bank of Canada.
Canada Auto Loan Rates Historical Data: Key Metrics and Sources
To understand the Canada auto loan rates historical data, it’s essential to examine reliable sources and metrics. Data from government and financial institutions provide a clear picture of rate fluctuations:
- Average Rates: Over the past 40 years, average historical car loan rates Canada have ranged from a high of 18% in the early 1980s to lows of 0-2% during promotional periods in the 2010s and early 2020s.
- Loan Terms: Shorter-term loans (e.g., 36 months) typically carry lower rates than longer terms (e.g., 72-84 months), which have become more common in recent years.
- Credit Impact: Borrowers with higher credit scores historically secured rates 1-2% lower than those with average or poor credit.
- Data Sources: The Government of Canada publishes economic reports that include lending rate trends, while bank websites like RBC and TD provide historical rate archives for auto loans.
This data underscores the importance of creditworthiness and loan term selection when evaluating financing options.
Past Auto Loan Rates in Canada Trends: Economic Drivers
Several economic factors have shaped the past auto loan rates in Canada trends:
- Bank of Canada Policy: The central bank’s overnight rate directly influences lending rates. For instance, rate hikes in 2022-2023 to combat inflation led to higher auto loan rates.
- Inflation: High inflation in the 1980s and 2022-2023 pushed rates upward, while low inflation in the 2010s kept rates affordable.
- Competition: Increased competition among banks, credit unions, and manufacturer financing (e.g., Toyota Financial Services) drove promotional rates, especially in the 2010s.
- Global Events: The 2008 financial crisis and the COVID-19 pandemic significantly altered lending landscapes, with stimulus measures lowering rates.
past auto loan rates in Canada trends, Understanding these drivers helps borrowers anticipate future rate changes and make informed decisions.
Evolution of Auto Loan Interest Rates in Canada: A Closer Look

The evolution of auto loan interest rates in Canada reflects advancements in financial systems and consumer behavior. In the 1980s, manual loan processing and limited competition kept rates high. By the 2000s, digital banking and automated underwriting lowered costs, enabling more competitive rates. The rise of online lenders and fintech platforms in the 2010s further disrupted the market, offering rates as low as 0% for promotional deals.
evolution of auto loan interest rates in Canada, Today, platforms like Quick Approvals streamline the loan application process, connecting borrowers with competitive rates tailored to their credit profiles. This evolution highlights how technology and competition have made auto financing more accessible.
Historical Average Auto Loan Rate Canada: Comparing Decades
The historical average auto loan rate Canada provides a benchmark for understanding affordability:
| Decade | Average Rate | Key Influences |
|---|---|---|
| 1980s | 15-20% | High inflation, tight monetary policy |
| 1990s | 8-12% | Economic recovery, declining inflation |
| 2000s | 6-9% | Stable economy, 2008 crisis impact |
| 2010s | 3-5% | Low interest rates, manufacturer promotions |
| 2020s | 1-8% | Pandemic stimulus, subsequent rate hikes |
This table illustrates the volatility of rates and their dependence on economic conditions.
Canada Historical Auto Loan Rates Chart: Visualizing Trends
Visualizing the Canada historical auto loan rates chart helps contextualize rate changes. While a graphical chart isn’t included here, historical data shows a clear downward trend from the 1980s to the 2010s, with periodic spikes during economic turbulence. For instance, rates surged in 2022-2023 as the Bank of Canada raised its key rate to combat inflation. Borrowers can access historical rate charts on bank websites or through financial platforms for detailed insights.
Why Did Auto Loan Rates Rise in Canada Historically: Key Factors
The question of why did auto loan rates rise in Canada historically can be answered by examining specific periods:
- 1980s Inflation Crisis: Double-digit inflation forced the Bank of Canada to raise rates, pushing auto loan costs to unsustainable levels.
- 2008 Financial Crisis Aftermath: While rates initially dropped, tighter lending standards in the recovery phase increased rates for subprime borrowers.
- 2022-2023 Inflation Surge: Post-pandemic supply chain disruptions and energy price spikes led to inflation, prompting rate hikes that impacted auto loans.
These periods highlight the interplay between macroeconomic policies and lending rates.
How to Access Historical Auto Loan Rates Canada: Practical Steps

For those wondering how to access historical auto loan rates Canada, several resources are available:
- Bank of Canada Archives: The Bank of Canada’s website provides historical interest rate data, including benchmark rates that influence auto loans.
- Financial Institutions: Major banks like Scotiabank and CIBC maintain records of past lending rates, often accessible through their customer service portals.
- Third-Party Platforms: Websites like Quick Approvals aggregate current and historical rate information, offering insights into trends.
- Government Reports: Statistics Canada publishes economic reports that include lending rate data, useful for academic or professional research.
These resources empower borrowers to make data-driven financing decisions.
Q&A: Common Questions About Historical Auto Loan Rates in Canada
What Are Historical Auto Loan Rates in Canada?

The historical auto loan rates in Canada have varied widely, from 15-20% in the 1980s to as low as 0-2% during promotional periods in the 2010s and early 2020s. These rates are influenced by the Bank of Canada’s monetary policy, inflation, and lender competition. For detailed data, the Bank of Canada offers historical rate archives.
How Have Auto Loan Rates Changed in Canada Over Time?

The how have auto loan rates changed in Canada over time question reveals a downward trend since the 1980s. High inflation drove rates to 15-20% in the 1980s, while economic stability and competition lowered them to 3-5% in the 2010s. Recent years saw fluctuations, with lows of 1-3% during the pandemic and rises to 5-8% by 2025 due to inflation.
Why Did Auto Loan Rates Rise in Canada Historically?
The why did auto loan rates rise in Canada historically question points to economic factors like inflation, monetary policy tightening, and global crises. For example, the 2022-2023 rate hikes followed inflationary pressures, as noted in government economic reports available at Government of Canada.
How to Access Historical Auto Loan Rates Canada?
To address how to access historical auto loan rates Canada, borrowers can consult Bank of Canada archives, bank records, or platforms like Quick Approvals. These sources provide comprehensive data on past rates, helping consumers understand trends and plan financing.
What Trends Can We Expect Based on Historical Average Auto Loan Rate Canada?
The historical average auto loan rate Canada suggests future rates will depend on economic conditions. If inflation stabilizes, rates may remain moderate (4-6%). However, global uncertainties or policy changes could push rates higher, as seen in the 2020s.
Conclusion
The historical auto loan rates in Canada offer a window into the economic forces shaping vehicle financing. From the high rates of the 1980s to the competitive lows of the 2010s, these trends reflect the interplay of inflation, monetary policy, and market dynamics. By understanding historical trends of auto loan rates in Canada, borrowers can better navigate today’s financing landscape. For further insights, explore authoritative resources like the Bank of Canada or connect with platforms like Quick Approvals to find tailored auto loan solutions. Stay informed and make strategic decisions to secure the best financing for your next vehicle purchase.


